To Fuse or Not to Fuse?
Puzzler 1
The split_stack function listed below takes a 1D tensor that logically represents a set of
independent features. It decomposes (“splits”) the 1D tensor into the individual features, performs
several common ML operations on them, and then reassembles (“stacks”) the individual results into a
single 1D tensor.
def split_stack(input_data, batch_size, input_dim):
split_input_data = torch.split(input_data, input_dim * batch_size)
layer_norm = torch.nn.LayerNorm(input_dim, eps=0.0, elementwise_affine=False, device='cuda:0')
norm_features = []
for i in range(len(split_input_data)):
features = split_input_data[i]
features_view = features.view([batch_size, input_dim])
norm_features_view = layer_norm(features_view)
tanh_norm_features = torch.tanh(norm_features_view)
norm_features.append(tanh_norm_features)
linear_input = torch.stack(norm_features)
linear_layer = torch.nn.Linear(input_dim, 1)
linear_output = linear_layer(linear_input)
return nn.functional.relu(linear_output)
num_inputs, batch_size, input_dim = 16, 1024, 256
input_data = torch.rand(num_inputs * batch_size * input_dim, device='cuda:0')
The following code is functionally identical to the code above, but it operates directly on the 3D tensor, i.e., avoids the calls to split and stack.
def combined(input_data, num_inputs, batch_size, input_dim):
features3d = input_data.view(num_inputs, batch_size, input_dim)
layer_norm = torch.nn.LayerNorm(input_dim, eps=0.0, elementwise_affine=False, device='cuda:0')
norm_features = layer_norm(features3d)
tanh_norm_features = torch.tanh(norm_features).view(num_inputs, batch_size, input_dim)
linear_layer = torch.nn.Linear(input_dim, 1)
linear_output = linear_layer(tanh_norm_features)
return nn.functional.relu(linear_output)
num_inputs, batch_size, input_dim = 16, 1024, 256
input_data = torch.rand(num_inputs * batch_size * input_dim, device='cuda:0')
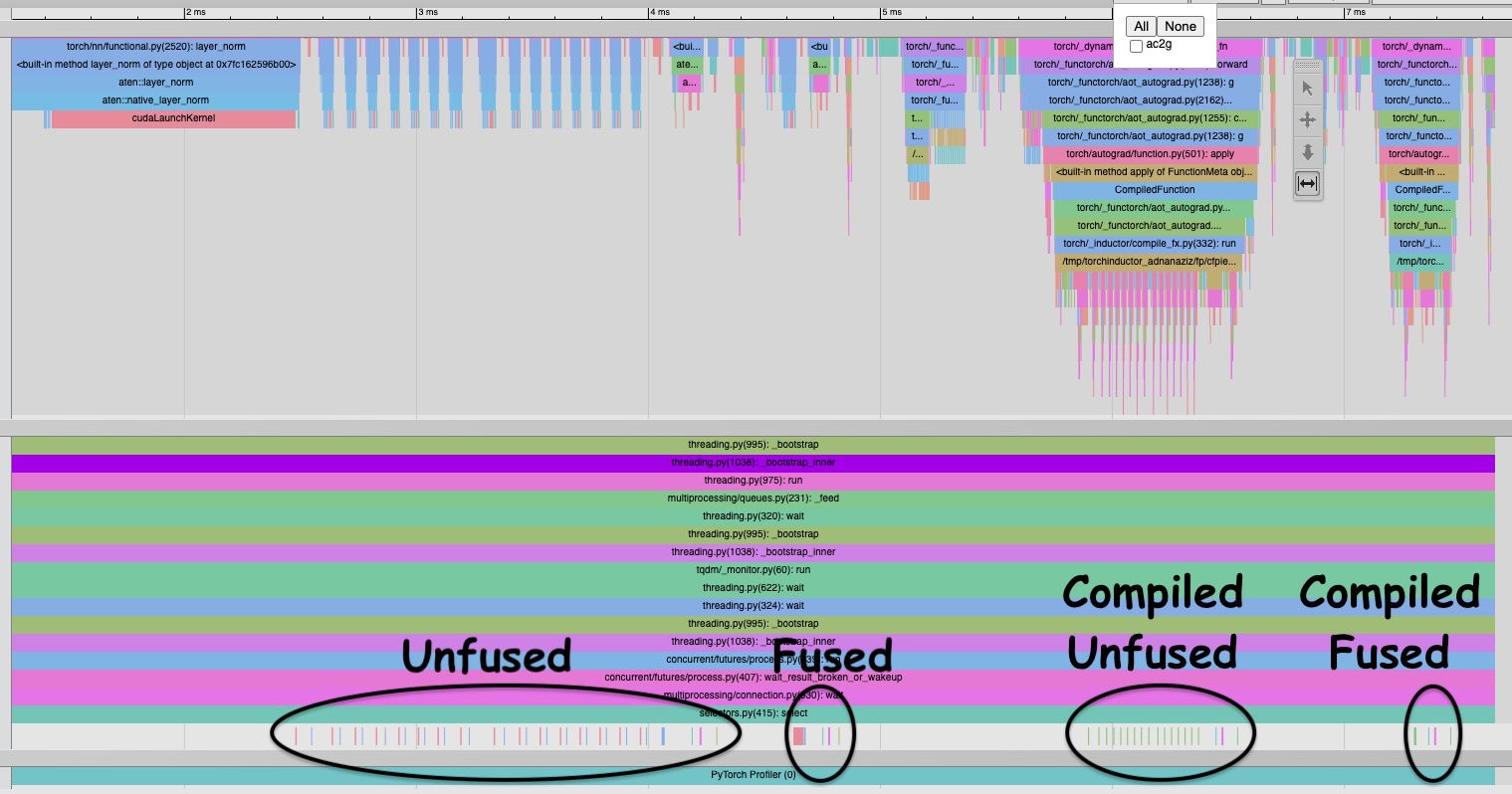
Empirically, combined is much faster than split_stack. As a concrete instance, with 16 input
features, a batch size of 1024, and input dimension of 256, combined is 8.4 times faster than
split_stack in terms of start-to-finish time on a 40 GB A100 GPU. Why?
Puzzler 2
We use PyTorch 2 to create compiled versions of the functions above:
compiled_split_stack = torch.compile(split_stack)
compiled_combined = torch.compile(combined)
Empirically, compiled_split_stack is 2.5 times faster and compiled_combined is 10.3 times faster than split_stack
in terms of start-to-finish time on a 40GB A100 GPU. Why?
PyTorch Profiler trace available here.